3D printers
Technologies
E-Nable devices must be printed on FDM (plastic fusion) printers.
Other technologies (resin for example) are not suitable.
Operating systems
3D printers can be driven either from Windows or MacOS, and most free slicing softwares also works under Unix.
We don’t know of any that work on Chromebooks, except of course online software.
Brands and models
All FDM printers are capable of printing e-Nable hands and arms.
The only really important criterion is the size of the bed which determines the dimension of the largest printable object.
A 20 * 20cm bed is big enough to make hands, to make arms you need a bed of at least 30 * 20cm.
A heated bed (and closed print volume) is required to print anything other than PLA.
Calibration
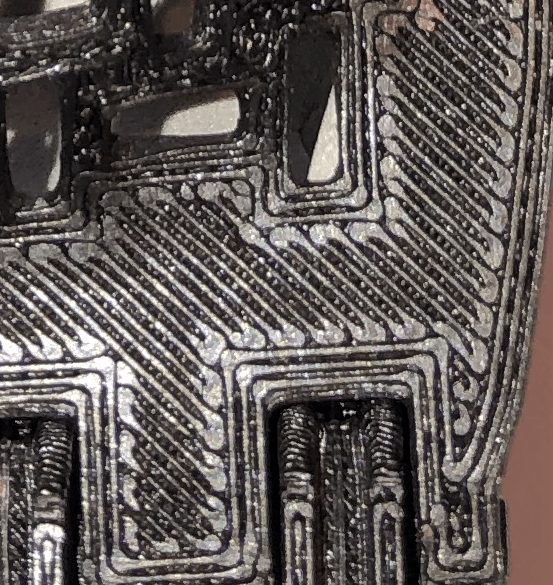
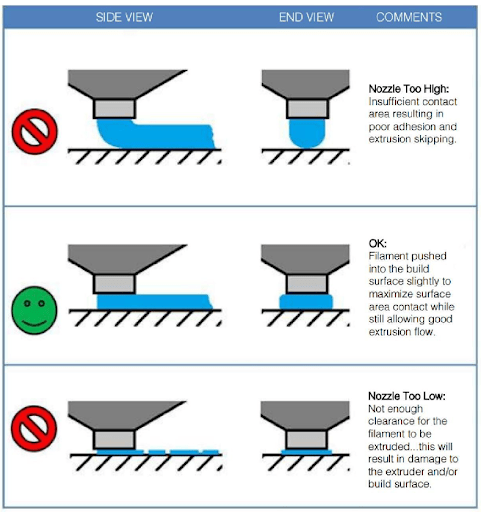
The first layer
The first layer is the key to a successful print. It ensures the adhesion of the part to the bed and determines the quality and appearance of the lower part of the part.
The distance from the nozzle to the bed is critical for a good first layer, which should be even in thickness, a little squashed but not too much.
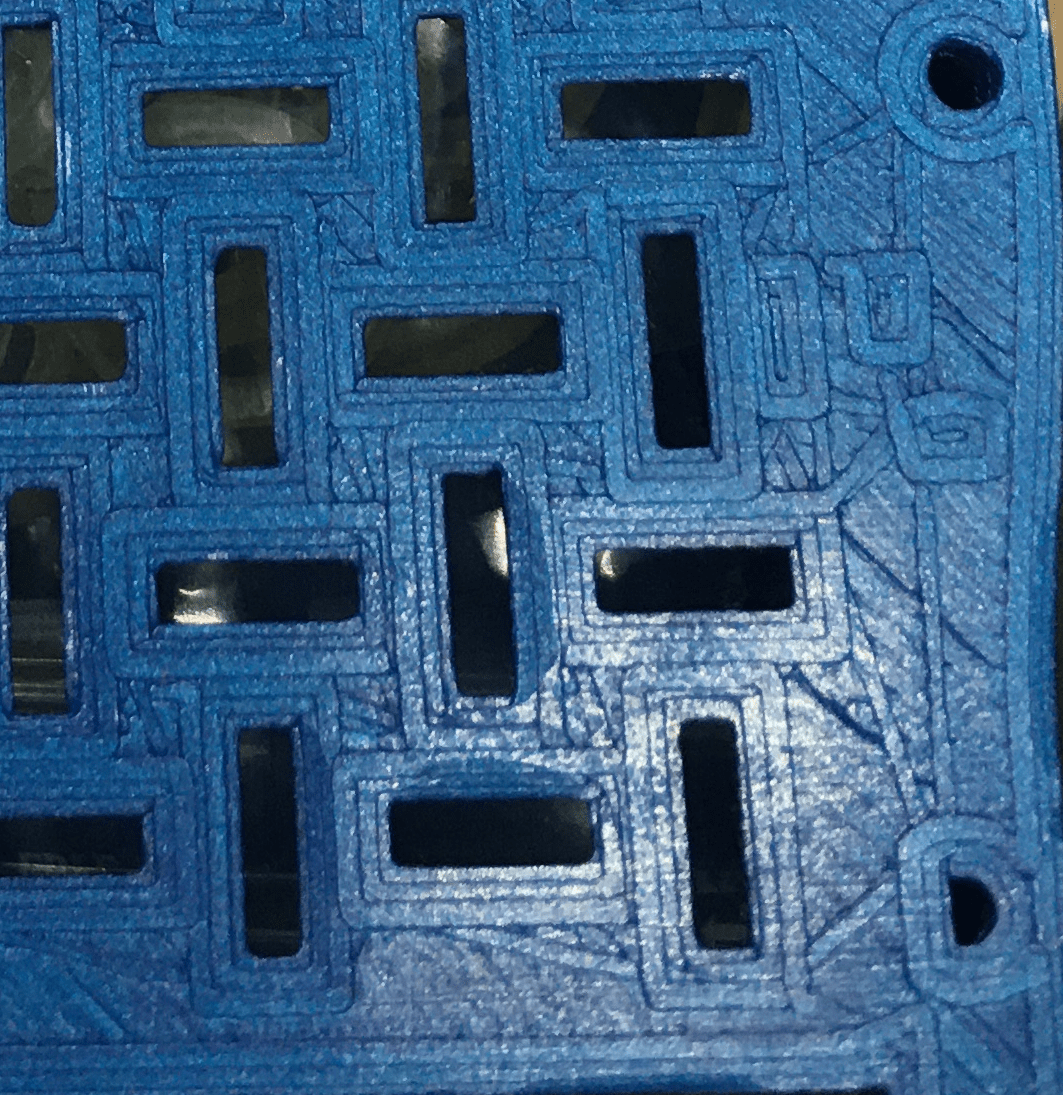
The parallel infill lines must touch each other along their entire length, and be in contact at their ends with the perimeter lines, without a gap or bulge.
Each printer and each slicer having different behaviors, we cannot go into the details of the configuration, but you can play with the thickness of the first layer, the flow, and the overlap between infill and perimeters.
Overhangs
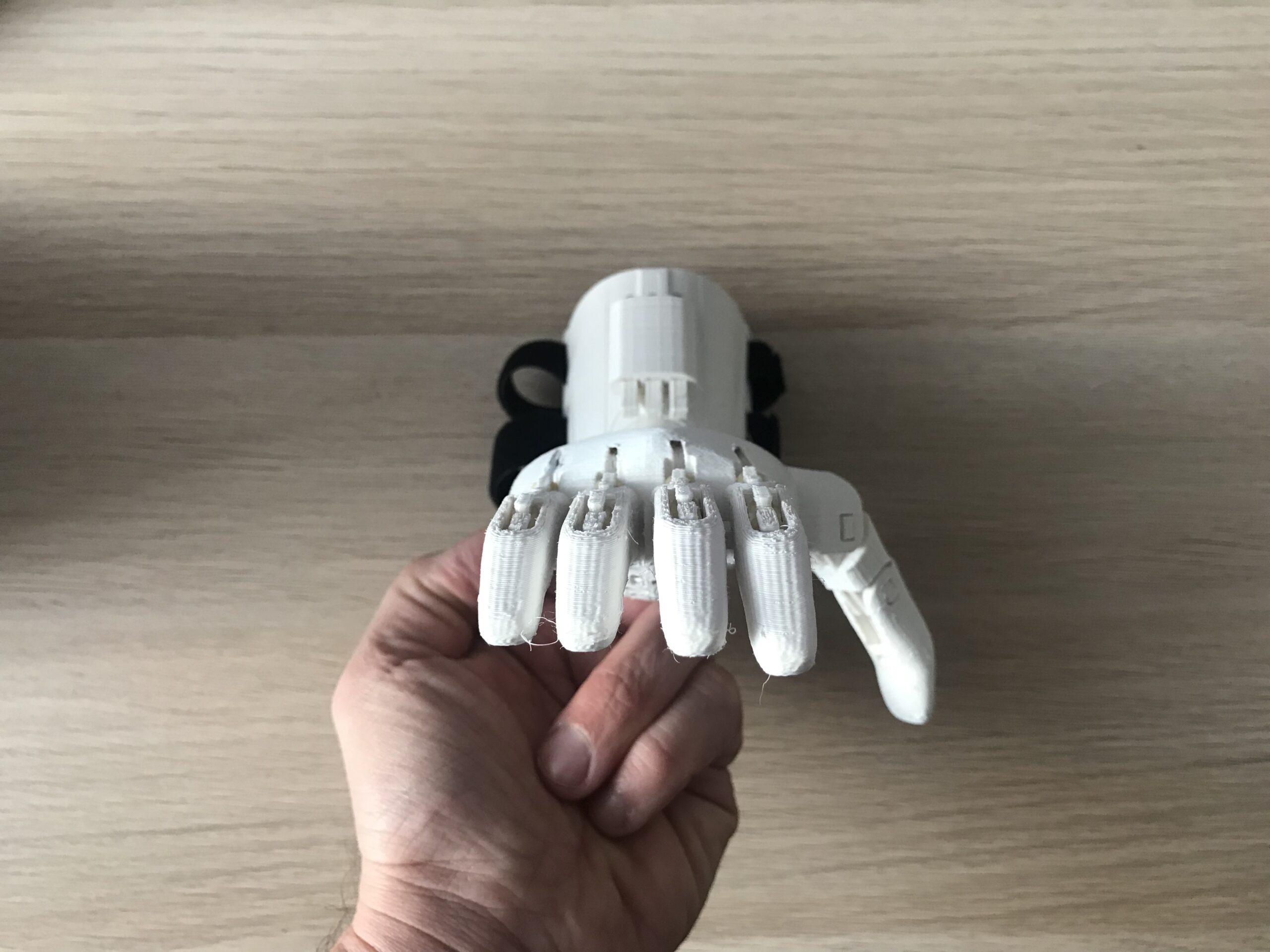
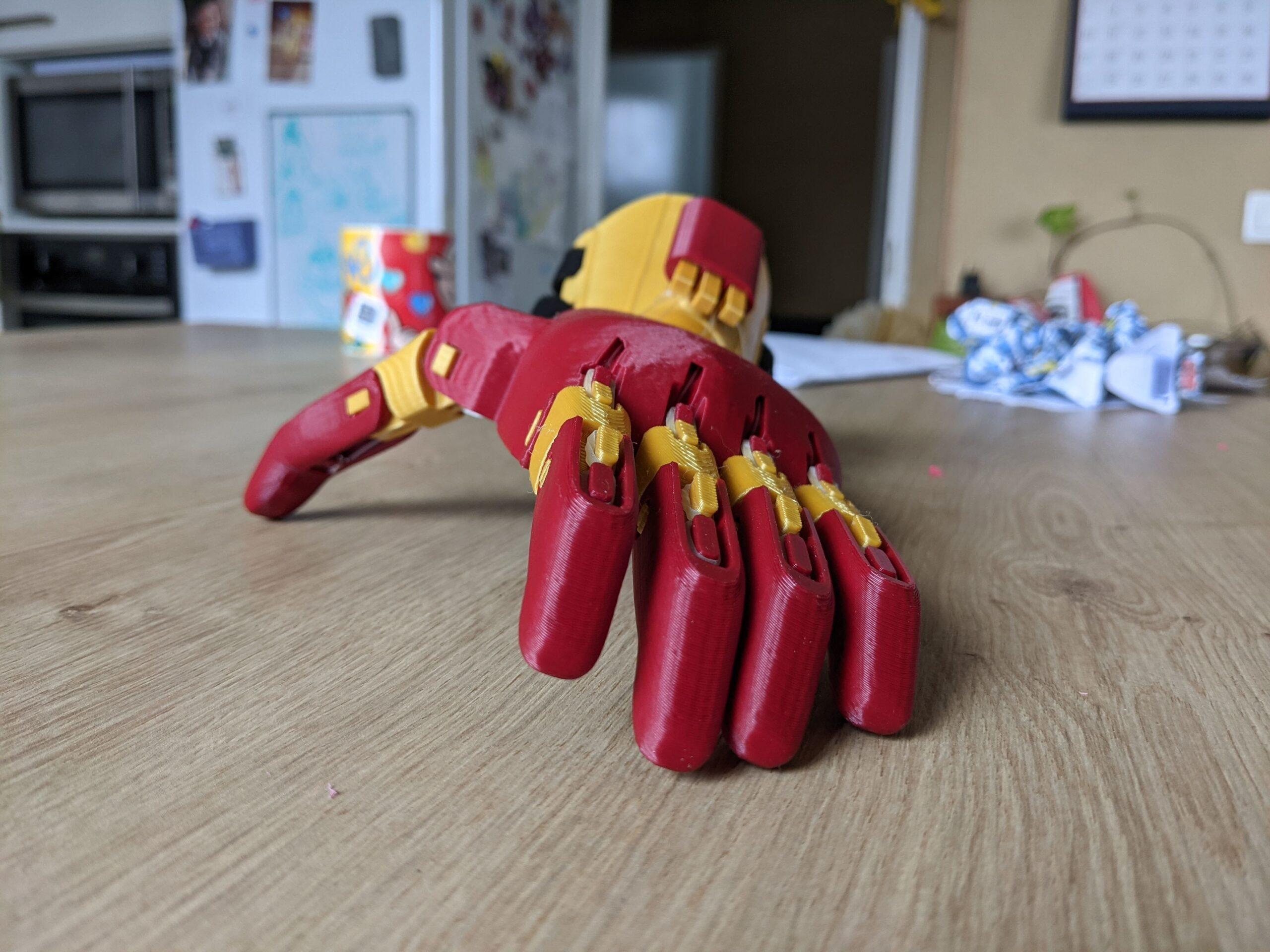
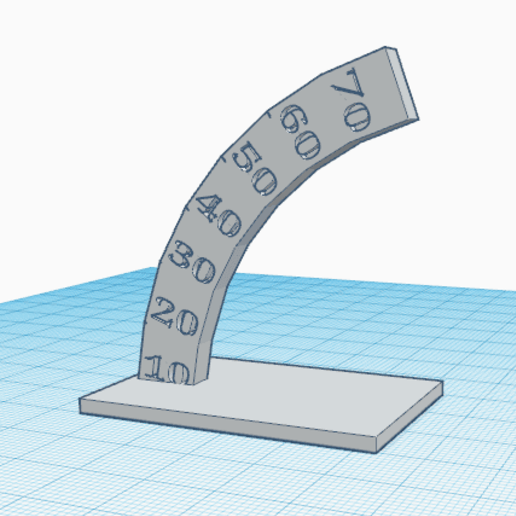
In the Phoenix hand, the tips of the fingers are printed with a fairly significant overhang. Check your printer settings by printing a test form or more simply just a fingertip.
You can often improve the quality of the overhangs simply by orienting the piece on the bed with the overhang toward the fan.